Study structure
The content on this page was translated automatically.
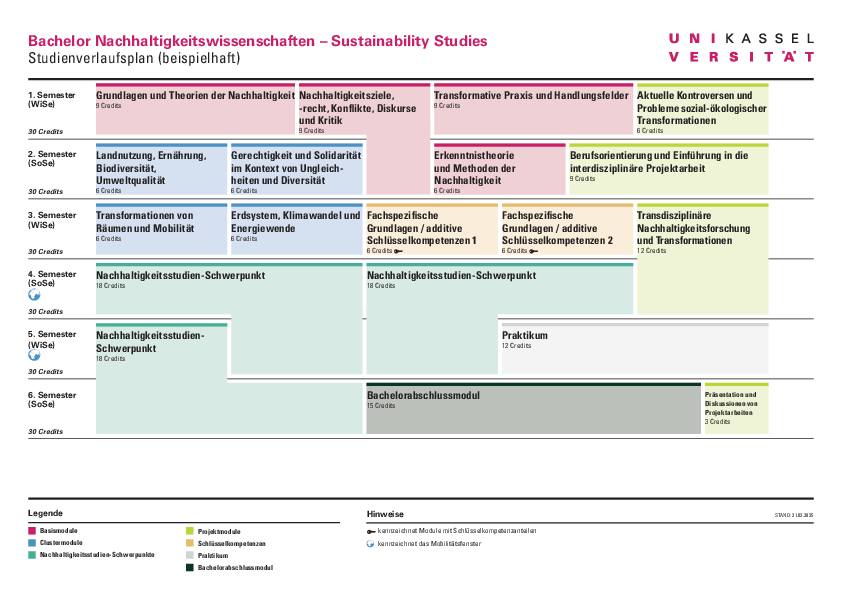
Overview
The basic modules teach fundamental theoretical and methodological knowledge about sustainability. You will receive an introduction to:
- central terms, theories and concepts of sustainability science,
- basic methods of interdisciplinary and transdisciplinary sustainability research,
- social conflicts and legal disputes in the field of sustainability,
- the connection between sustainability and transformation processes.
- In addition, students learn the techniques of scientific work.
The cluster modules deal with specific challenges and needs of the socio-ecological transformation. You will deal with four central topics:
- Land use, food, biodiversity and environmental quality - effects of human intervention on ecosystems and solution strategies for sustainable use.
- Justice and solidarity in the context of inequalities and diversity - social dimensions of sustainability, distribution issues and ethical aspects.
- Transformations of spaces and mobility - sustainable urban and spatial planning and mobility concepts.
- Earth system, climate change and energy transition - physical principles, climate policy and sustainable use of resources.
The practice-oriented project modules enable you to apply the knowledge you have acquired in interdisciplinary teams. You will work on sustainability-related issues and develop solutions for current challenges of socio-ecological transformation. You will learn
- interdisciplinary project work and methods of sustainability research,
- develop practical solutions for real-world problems,
- get to know career prospects in the field of sustainability.
- In addition, students present the project results to specialist groups and the public.
Students choose three focus areas from 31 possible specializations (54 ECTS credits in total). These focus on sustainability issues from a specific specialist perspective. Possible specializations:
- Human scientific prerequisites for sustainable development
- Human-nature relations (philosophy)
- Sustainability communication and social participation
- Sustainability communication in crisis discourses
- Sustainability communication on cultural norms and values
- Genesis and structures: sustainability concepts and nature relations
- Processes and consequences: Diversity, globalization and solidarity
- Actors and practices of socio-ecological transformations
- Sustainable, energy-efficient buildings
- The green, climate-friendly city
- Socially just urban development
- Biological principles of sustainability - molecular biology
- Biological principles of sustainability - ecology & botany
- Mathematical foundations for SDG considerations
- Sustainability in chemical-physical applications
- Ecological agricultural systems
- Organic agriculture and society
- Mobility and transportation
- Water management
- Sustainable material cycles and product life cycles
- Environmental economics
- Sustainability management
- Environmental sustainability law
- Social sustainability law
- Sustainability studies on electrical energy technology
- Computer science: people and society
- Artificial intelligence and data science
- Computer Science: Safety and Reliability
- Critical Sustainability in Art and Design
- Transformative project management
- Sustainability discourses and fields of action