Study structure
The content on this page was translated automatically.
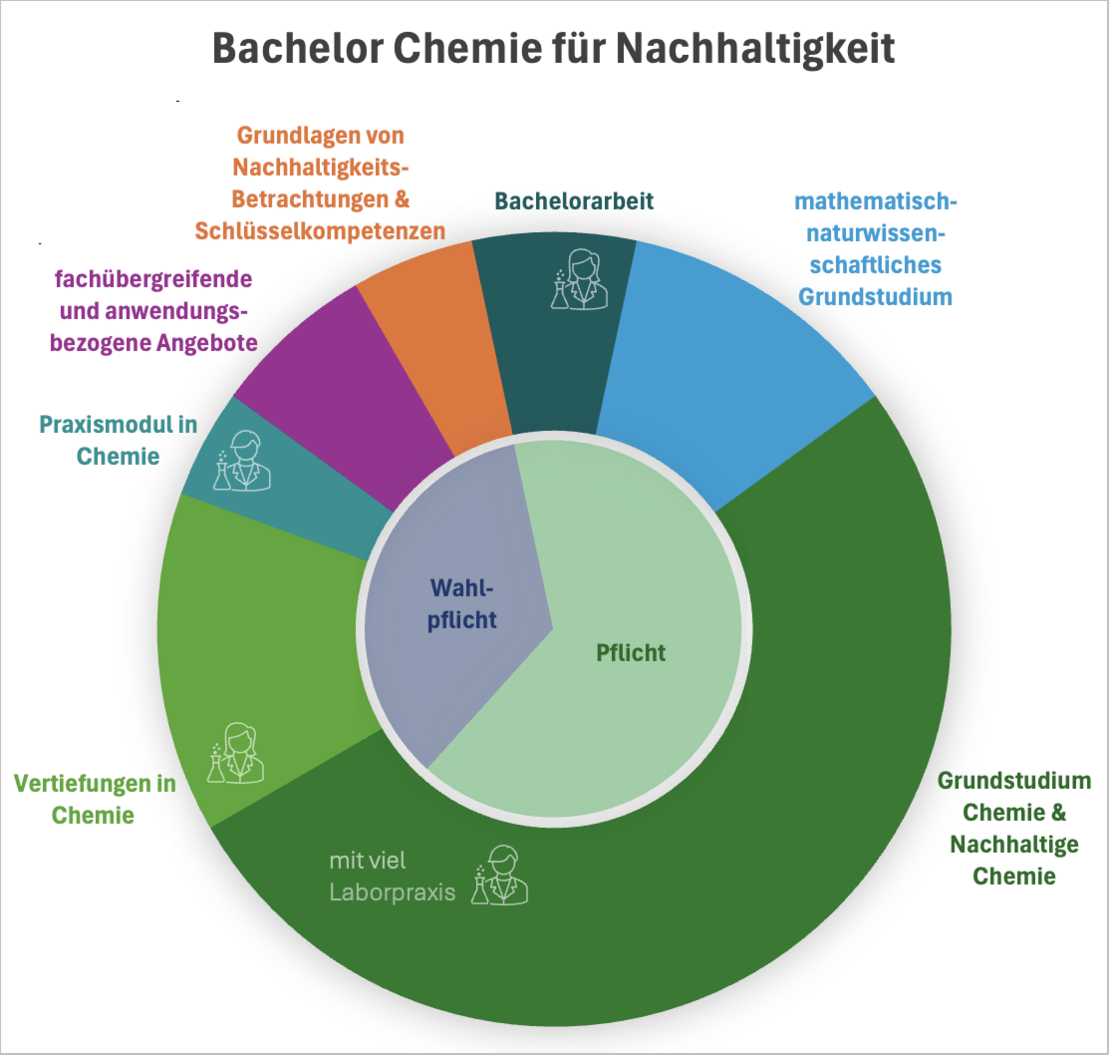
Your Bachelor's degree program consists of several modules, which usually end with an exam. Some modules are compulsory, but you can also pursue your personal interests with numerous compulsory electives and create your own individual timetable.
Course content & components
Here you will learn or consolidate the basic knowledge of mathematics, physics and biology that you will need for your chemistry degree.
Choose between various courses on sustainability concepts, strategies, discourses and analyses, global material cycles, etc., which lay the foundation for a holistic understanding of sustainability.
You can gain further key skills for your studies and future career through courses on scientific work, programming or foreign languages, for example.
The basic chemistry course includes general chemistry, inorganic chemistry, organic chemistry, theoretical chemistry, physical chemistry, biochemistry, toxicology and synthetic chemistry.
The lectures are usually combined with exercises, seminars and laboratory practice.
Once you have built up your basic knowledge, you will focus on the principles of green chemistry and aspects of sustainable chemistry. You can choose between two course combinations that offer you insights into either industry or nanostructure science.
Finally, in Sustainable Chemistry, you will learn research-related content from the areas of more sustainable synthesis, energy storage and bio-based materials.
In this area, you can choose from a variety of courses according to your interests - e.g. materials chemistry, computational chemistry or photochemistry.
Broaden your perspectives with related and application-oriented courses from the neighboring sciences - e.g. with water chemistry, construction chemistry, life cycle assessments, resource management and much more.
Prepare for your career with a professional internship or a research internship.
At the end of your studies, demonstrate that you can independently work on and present a project related to current issues in sustainable chemistry.